Momen Abayazid received his M.Sc. in Biomedical Engineering at Delft University of Technology and his PhD in surgical robotics at the University of Twente. In 2015, Momen Abayazid has been a postdoctoral research fellow Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston MA, USA. He worked on several projects related to robotic image-guided needle insertion and motion compensation using machine learning. Since 2017 he has been faculty member as an assistant professor in the Robotics and Mechatronics group (RaM). He is involved in different projects related to Robotics for medical applications, Soft Robotics and image-guided interventions. He is also involved in teaching BSc and MSc courses such as Signals, Image processing and computer vision.
Google Scholar: https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=NCmEDAMAAAAJ
Research Gate: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/M_Abayazid
Expertise
Computer Science
- Needle Insertion
- Control
Medicine and Dentistry
- Endoscope
- Tactile Feedback
- Evaluation Study
Engineering
- Haptics
- Modules
- Pneumatics
Organisations
Publications
2025
2024
2023
Research profiles
Momen Abayazid is involved in teaching BSc and MSc courses such as Signals, Image processing and computer vision. Currently, he is a member of the Educational Quality Committee of Bachelor program of electrical engineering at the University of Twente.
Affiliated study programs
Courses academic year 2025/2026
Courses in the current academic year are added at the moment they are finalised in the Osiris system. Therefore it is possible that the list is not yet complete for the whole academic year.
- 191211208 - Internship EE
- 191211219 - Master Thesis Project
- 191211650 - Multi-Disciplinary Design Project
- 193650999 - Masters Assignment
- 201100179 - Graduation Project
- 201400462 - Internship S&C
- 201600187 - Individual Project
- 201800207 - Capita Selecta RaM
- 201900223 - Capita Selecta Electrical Engineering
- 202001162 - Bachelor Thesis EE
- 202001434 - Internship EMSYS
- 202200120 - Internship ROB
- 202200122 - MSc-Thesis Project
- 202300070 - Final Project EMSYS
- 202300349 - Internship ROB / ME
- 202400318 - M12 BSc Assignment BMT
- 202500385 - Internship ROB / AM
Courses academic year 2024/2025
- 191211208 - Internship EE
- 191211219 - Master Thesis Project
- 191211650 - Multi-Disciplinary Design Project
- 193650999 - Masters Assignment
- 201100179 - Graduation Project
- 201400462 - Internship S&C
- 201600187 - Individual Project
- 201800207 - Capita Selecta RaM
- 201900223 - Capita Selecta Electrical Engineering
- 202001162 - Bachelor Thesis EE
- 202001434 - Internship EMSYS
- 202200103 - Image Processing and Computer Vision
- 202200120 - Internship ROB
- 202200122 - MSc-Thesis Project
- 202300070 - Final Project EMSYS
- 202300349 - Internship ROB / ME
- 202400318 - M12 BSc Assignment BMT
- 202400681 - AI- and Image-guided Robotics
Momen Abayazid is involved in different projects related to Robotics for medical applications, Soft Robotics and image-guided interventions.
Current projects

TERRINET
The European Robotics Research Infrastructure Network
The European Robotics Research Infrastructures Network (TERRINet) project aims at building a world-class network with harmonised services and complementary capabilities where talented researchers from academia and industry worldwide will have access and will be able to explore new ideas and establish personal and joint projects; to get in contact with and be inspired by leading and creative scientists, technologists, experts and industrial representatives; to share information and gain knowledge for boosting their scientific research and potential for technological innovation. The plan of TERRINet is to accomplish its vision by providing not only an organised and well orchestrated set of facilities, but also databases, tools and methodologies which will remain operational after the end of the project, so to provide a long-term service to Robotics science and industry in Europe and worldwide.

ASSIST
Automation, Surgery Support and Intuitive 3D visualization to optimize workflow in IGT SysTems
Current software image-guided therapy applications to assist the physician still require significant manual user interaction while all attention should go to the patient instead. The ASSIST project will develop technologies and solutions to get the physician back in control of the clinical procedure by assisting or automating part of the physician’s tasks during image-guided therapy procedures. The aim of the project is to optimise and simplify the workflow in image-guided therapy procedures with the main goal of streamlining physicians’ work, optimising imaging systems, improving patient outcomes, reducing human error and lowering costs.

IMPACT
Intelligence based iMprovement of Personalized treatment And Clinical workflow supporT
Healthcare faces many challenges like improving patient outcome and working more cost-effectively in the face of growing demand, declining staff capacity and the rapid succession of new clinical and technological developments. The IMPACT project will address these challenges by building on preceding ITEA projects like MEDIATE and BENEFIT to add the next logical step: from evidence-based towards intelligence-based healthcare. To achieve intelligence-based healthcare the IMPACT project will promote automatic data collection and artificial intelligence throughout the complete clinical pathway. To achieve intelligence-based healthcare the IMPACT project will promote automatic data collection and artificial intelligence throughout the complete clinical pathway, i.e., from hospitalization to patient release: 1. Personalized treatment planning for optimal treatment of each individual patient and thereby improve patient outcome and cost efficiency. This is only possible when all relevant data available is made available and analyzed intelligently using e.g. Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, etc. 2. Industrialized treatment to reduce preventable medical error and improve predictability and efficiency of clinical procedures. Reproducibility is key which can be accomplished by robotic tools, real-time navigation imaging and strictly adhering to medical guidelines and protocols. 3. Workflow optimization at various levels (hospital, room, table side) to remove waste and inefficiency in the healthcare system. This is done by intelligent data-driven analysis (e.g. Deep Learning) considering all relevant data streams to take the right decision at the right moment concerning the patient, the staff and the equipment. The IMPACT consortium covers all healthcare stakeholders with a good balance between research-oriented partners, technology suppliers, industrial end-product suppliers and clinical end users. This project is part of European consortium that includes industrial, clinical and academic partners from the Netherlands, Sweden and Belgium.
MRI-guided Irreversible Electroporation
Image guided irreversible electroporation of cancerous tissue in a MRI environment
Finished projects
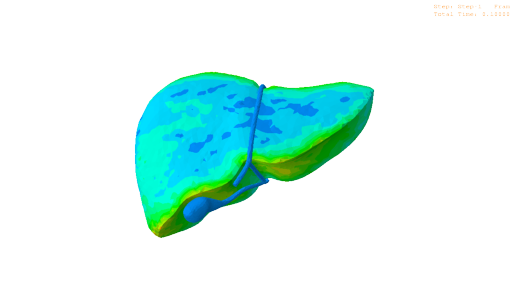
Soft Robotics
n percutaneous interventions for hepatic tumor treatment, organ motion caused by respiration can lead to inaccurate needle placement hence less effective therapeutic and diagnostic outcome. The aim of this project is to use soft robotics techniques to develop an actuated phantom that mimics respiratory motion in liver for needle insertion procedures.
In the press
- https://www.azorobotics.com/News.aspx?newsID=7652
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/releases/298693.php
News on utwente.nl
Address

University of Twente
Carré (building no. 15), room C3607
Hallenweg 23
7522 NH Enschede
Netherlands
University of Twente
Carré C3607
P.O. Box 217
7500 AE Enschede
Netherlands